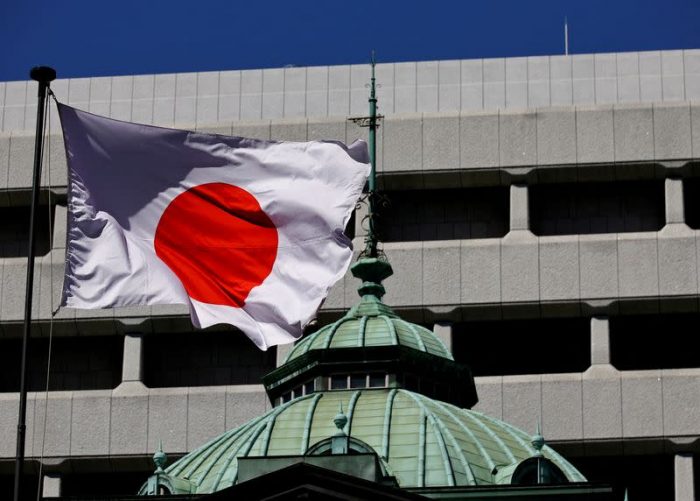
Financial institution of Japan introduced a brand-new strategy Tuesday to reduce following year’s annual report, as it is because of boosted international threats, such as combating between East and tolls enforced by the Trump management.
The marketplace for Japanese federal government bonds (JGB) is normally tranquil, yet has actually stood out in current weeks as a result of the rise in returns, which has actually increased cautions for greater financial debt federal governments.
Last month, Super JGB’s return struck document degrees, suggesting greater loaning expenses for the federal government and necessity for the Financial institution of Japan (BOJ) and the Treasury to maintain the marketplace.
See likewise: Taiwan Blacklist Chinese chip manufacturer Huawei, weak
Regularly tighten up to progressively slim
After years of financial stimulation to sustain Japan’s flag economic climate, the shed has actually bought majority of all JGB and is currently attempting to beautifully Lower those holdings throughout a procedure called measurable tightening up
According to a strategy created last July, the shed reduced its regular monthly bond acquisitions by concerning 400 billion yen ($ 2.76 billion) quarterly.
As A Result, in the present quarter, the reserve bank bought 41 trillion yen of JGB monthly, below 4.5 trillion yen monthly from January to March.
The shed claimed the steady decrease price will certainly be lowered to a 200 billion yen price adjustment per quarter beginning with April following year.
The reserve bank likewise chose to enable capitalists to preserve even more 10-year notes via its funding centers. The action is anticipated to enhance market liquidity and increase bond divestitures of bond destruction.
$ 9 trillion in arrearage
Japan has around 1.3 billion yen ($ 9.07 trillion) of superior protections, the 2nd biggest financial debt worldwide, behind the United States Treasury market of $28.2 trillion.
The recurring monetary deficiency has actually brought about a growth of Japan’s debt-to-gross residential item (GDP) proportion to around 250%, the highest possible amongst established nations. Head Of State Shigeru Ishiba claimed last month that the nation’s monetary circumstance is even worse than that of Greece
Nevertheless, unlike Greece, Greece’s debt-to-GDP proportion was around 2010, when the nation was launched on bond, concerning 150% of its Japanese financial debt was held locally. This makes the JGB market much less susceptible to international capitalists that penalize the federal government by offering financial debt, supposed bond vigilants.
Capitalists watch out for huge shortages
The current bonds have actually offered out in current weeks as a result of capitalists’ issues concerning significant providers’ monetary shortages and financial debt heaps, which are issues concerning Moody’s downgrade to the united state on Might 17.
However Japan has some one-of-a-kind issues. Participants are taking into consideration bring in cash money prep work and various other stimulation actions in advance of your house of Lords political election in July. Furthermore, need for incredibly bonds amongst standard customers has actually likewise decreased.
For instance, Japanese life insurance policy business have actually gradually bought these protections in the last few years to adhere to brand-new solvency laws. As a lot of the acquisitions are being bought, insurer are currently transforming to greater financial debt.
The 20-year JGB public auction held last month disclosed an instability. Need is the weakest given that 1987, as revealed by the tail of the public auction– the distinction in between the most affordable and ordinary appropriate rates.
This set off a lasting financial debt sell-off.
This brings 40-year accept a document 3.675%, 30-year accept an all-time height of 3.185%, while 20-year accept 2.595%, the highest possible given that October 2020.
The succeeding 30 and 40 years of protections sales likewise revealed weak need, stimulating issues concerning boosted loaning expenses.
boj concern much shorter bonds
The fast upgrade of JGB has actually created unusual plan manufacturers. Over the previous couple of years, the reserve bank of Japan has actually conserved the unstable market by purchasing bonds and supplies.
However, under Guv Kazuo Ueda Boj has actually devoted to reducing annual report leaving the Treasury leads in a tranquil market.
Money Priest Katsunobu Kato alerted that greater rates of interest might additionally endanger Japan’s economic circumstance and assured “suitable” financial debt monitoring. The federal government provided an uncommon caution in its financial roadmap last Friday.
Ueda recognizes that need for ultra-long bonds has actually decreased, and these volatility in returns might impact much shorter rates of interest, which will certainly have a much more straight financial effect.
The Treasury Division is currently preparing to reduce 20-year, 30-year and 40-year bonds, stabilizing these lowered bonds with a boost in much shorter notes, Reuters reported. The ministry is likewise taking into consideration redeeming some extra-long JGBs.
Climbing returns suggest JGB is coming to be progressively appealing to abroad capitalists, specifically those seeking to minimize their direct exposure to the buck. Nevertheless, international owners are more probable to turn and drain towards the marketplace, triggering volatility.
Gatto spoke about the significance of residential possession of residential financial debt in current days and recommended a brand-new sort of drifting notes that enable unpublished business to buy bonds created for private capitalists.
The Treasury will certainly meet market individuals later on this month, which will certainly educate its choices on bond issuance and redeemed modifications.
The 20-year JGB public auction on June 24 will certainly be the following crucial examination of the need for ultra-long bonds.
- Jim Pollard’s added editor Reuters